Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the de-facto Inter-Domain Routing/EGP protocol
BGP provides each AS a means to:
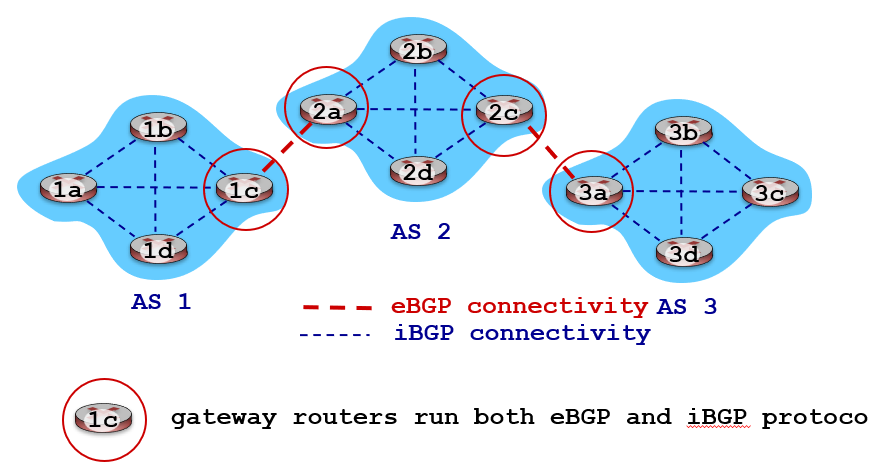
- eBGP (exterior BGP): Obtain subnet reachability information from neighboring ASes
- iBGP (internal BGP): Propagate reachability information to all AS-internal routers
- Determine “good” routes to other networks based on reachability information and policy
Allows subnets to advertise their existence to rest of Internet
BGP session:
- Two BGP routers (peers) exchange BGP messages over semi-permanent TCP connection
- Advertising paths to different destination network prefixes (BGP is a path vector protocol)
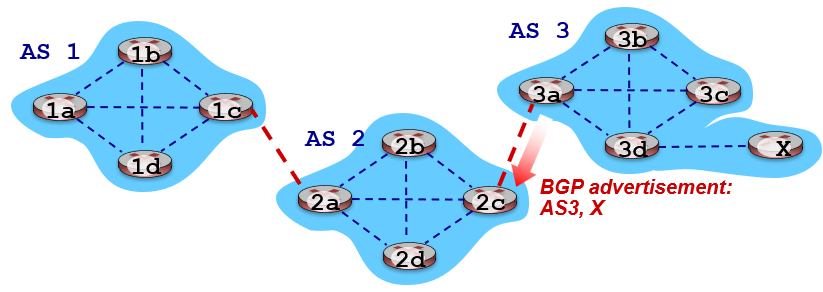
- When AS3 gateway router 3a advertises path
AS3,Xto AS2 gateway router 2c,- AS3 promises to AS2 that it will forward datagrams towards X
Path attributes and BGP routes
- Advertised prefix includes BGP attributes
- Prefix + attributes = route
- Two important attributes:
AS-PATH: list of ASes through which prefix advertisement has passedNEXT-HOP: indicates specific internal-AS router to next-hop AS
- Policy-based routing:
- Gateway receiving route advertisement uses import policy to accept/decline path (e.g. never route through AS Y)
- AS policy also determines whether to advertise path to other neighboring ASes
BGP path advertisement
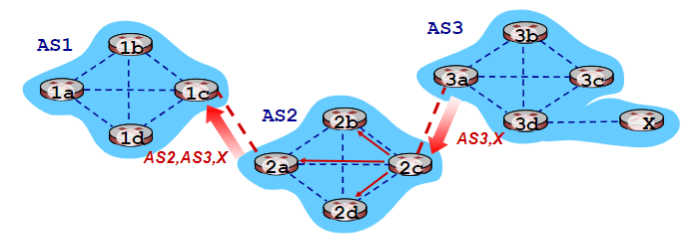
- AS2 router 2c receives path advertisement
AS3,X(via eBGP) from AS3 router 3a - Based on AS2 policy, AS2 router 2c accepts path
AS3,Xand propagates (via iBGP) to all AS2 routers - Based on AS2 policy, AS2 router 2a advertises (via eBGP) path
AS2,AS3,Xto AS1 router 1c
TODO take notes on BGP path advertisement (see lecture 24)
BGP, OSPF, forwarding table entries
How does router set forwarding table entry to distant prefix?
TODO take notes (see start of lecture 25)
BGP Route Selection
Router may learn about more than one route to destination AS, selects route based on:
- Local preference value attribute: Policy decision
- Shortest
AS_PATH - Closest
NEXT_HOProuter: Hot Potato Routing - …additional criteria
Nontransit vs Transit ASes
- Internet service providers often have transit networks
- Nontransit AS might be a corporate or campus network
- Could be a content provider
Traffic is never supposed to flow from an ISP (transit network) through a nontransit AS to another ISP (also a transit network)
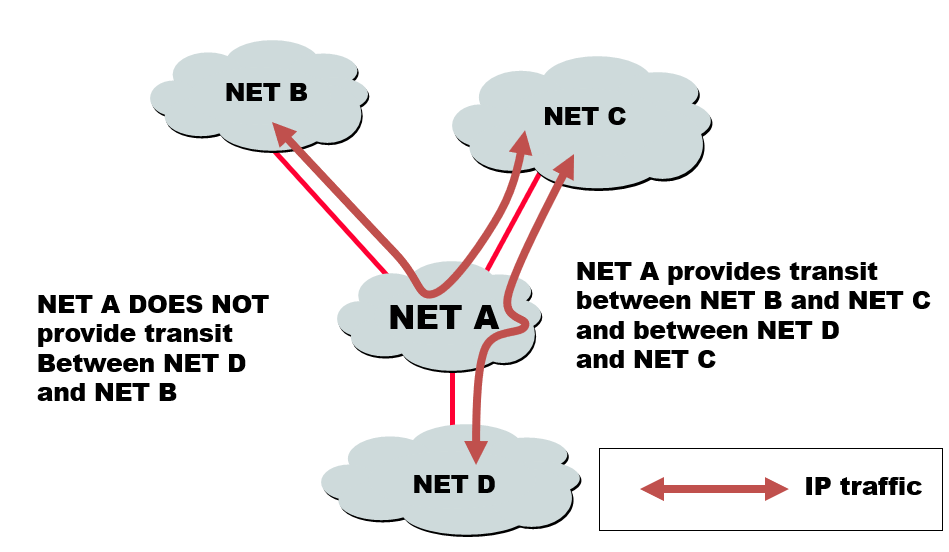
Selective Transit
Most transit networks transit in a selective manner
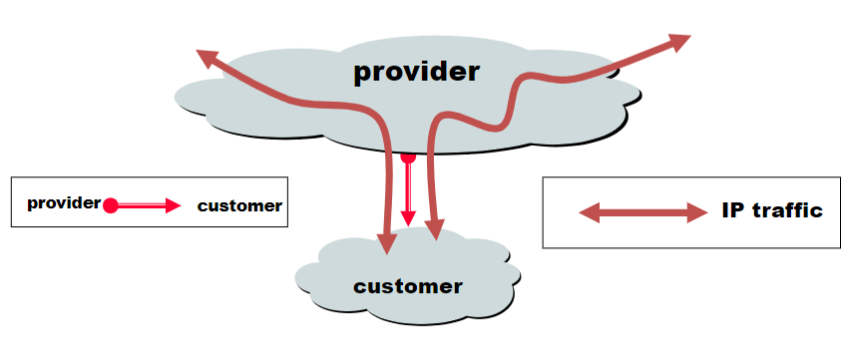
Customers and Providers
Customer pays provider for access to the Internet
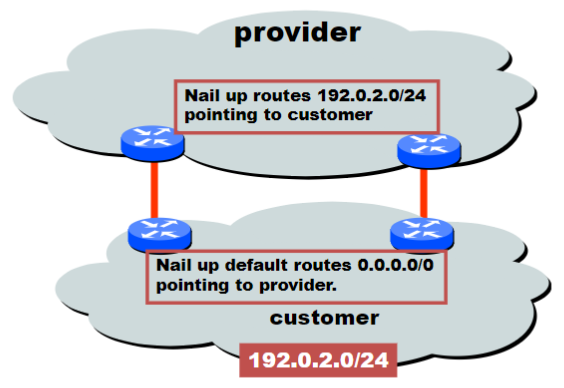
Customers don’t always need BGP
- Static routing is the most common way of connecting an autonomous routing domain to the Internet
Customer-provider hierarchy:
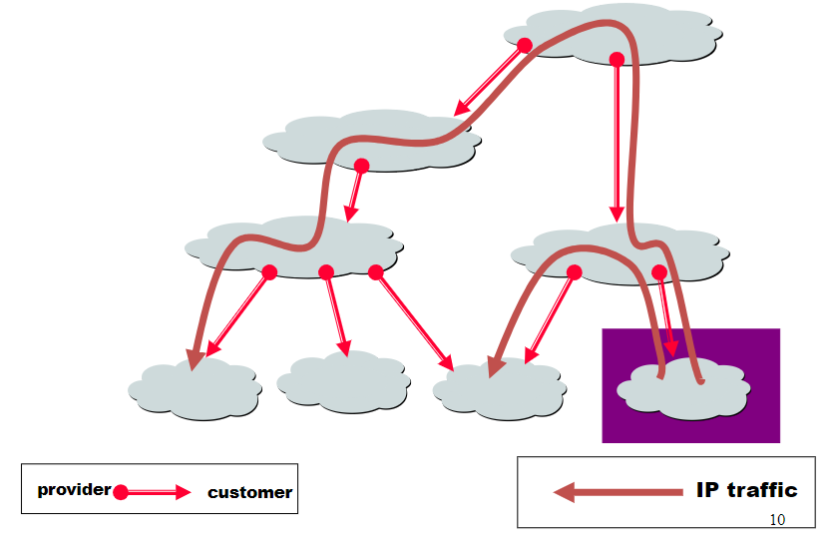
The Peering Relationship
- Peers provide transit between their respective customers
- But they don’t provide transit between peers
- Often don’t exchange money to help each other out
- If they didn’t provide transit between their customers, Internet would become disconnected
- Hence, they do it for free
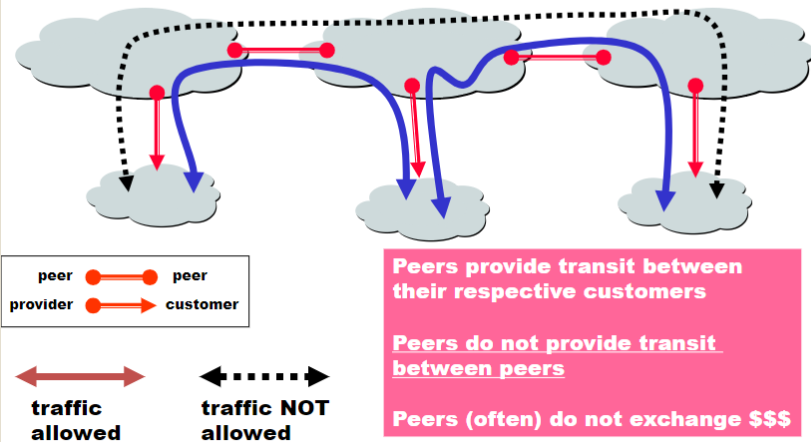
Peering provides shortcuts
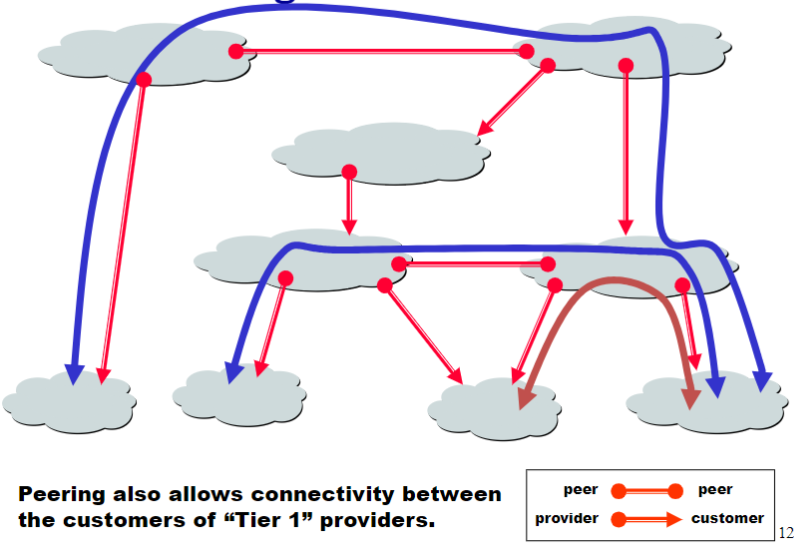
Peering also allows connectivity between the customers of Tier 1 providers
BGP Operations Simplified
- Establish BGP session on TCP port 179
- Exchange all active routes
- While connection is alive, exchange incremental route update messages
Four Types of BGP Messages
- Open: Establish a peering session
- Keep alive: Handshake at regular intervals
- Notification: Shuts down a peering session
- Update: Announcing new routes or withdrawing previously announced routes Announcement = Prefix + Attribute values
BGP Attributes
Most important attributes:
AS_PATHNEXT_HOPMULTI_EXIT_DISCLOCAL_PREFCOMMUNITYORIGINATOR_IDCLUSTER_LIST
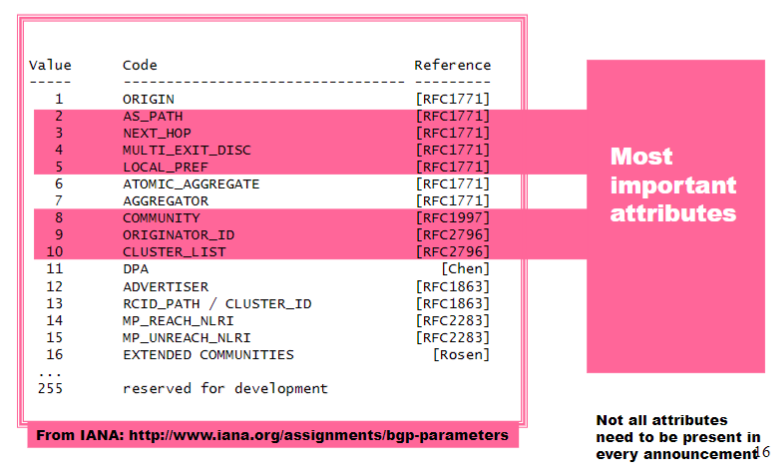
Attributes are used to select best routes
- Given multiple routes to the same prefix, a BGP speaker must pick at most one best route
- It could reject them all
Next Hop attribute: Every time a route announcement crosses an AS boundary, the Next Hop attribute is changed to the IP address of the border router that announced the route
Join EGP with IGP for Connectivity
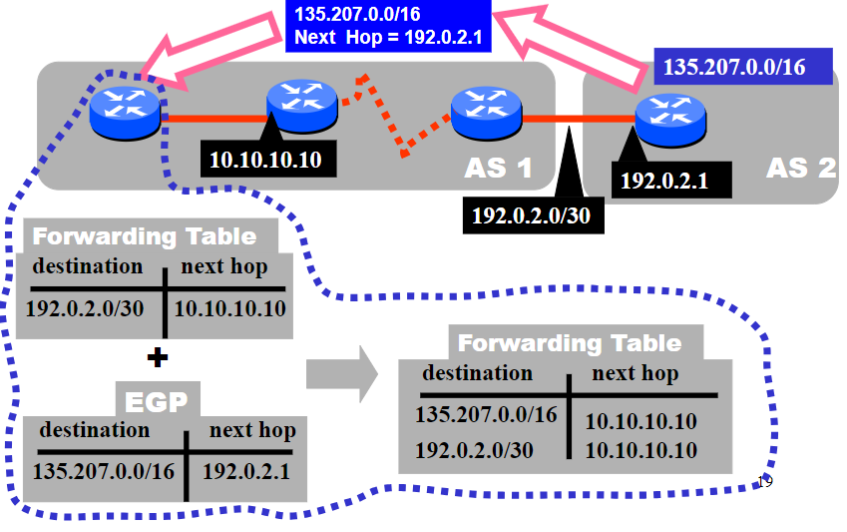
Implementing customer/provider and peer/peer relationships
Two parts:
- Enforce transit relationships
- Outbound route filtering
- Enhance order of route preference
- Provider < peer < customer
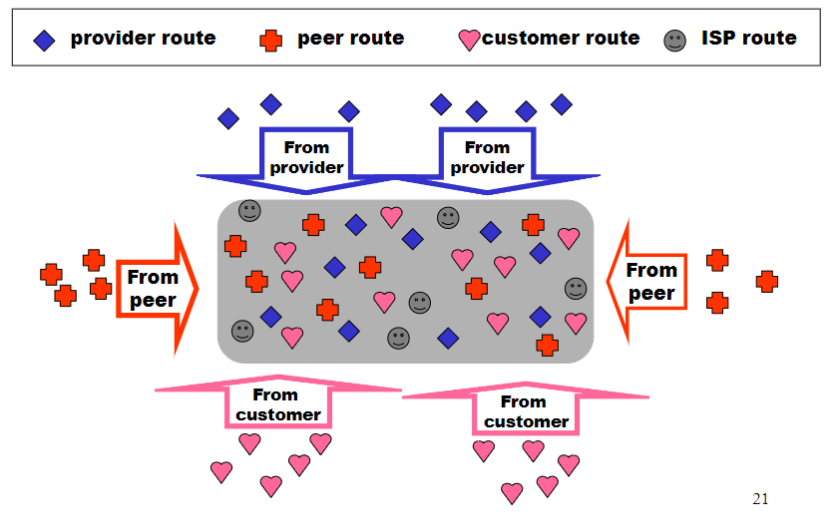
Import Routes
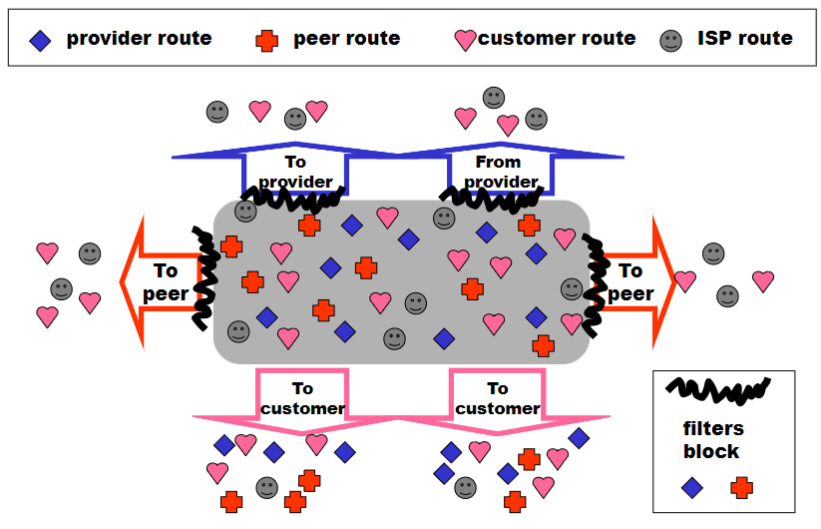
Export Routes
BGP Communities
BGP communities are how routes are colored
- A community value is 32 bits
- By convention, first 16 bits are ASN indicating who is giving it an interpretation
- Second 16 bits are community number
- Community values used for signaling within and between ASs
- Very powerful because it has no predefined meaning
Community attribute: a list of community values
- So one route can belong to multiple communities
Two reserved communities:
no_export=0xFFFFFF01: don’t export out of ASno_advertise=0xFFFFFF02: don’t pass to BGP neighbors
Tweak Tweak Tweak
For inbound traffic:
- Filter outbound routes
- Tweak attributes on outbound routes in the hope of influencing your neighbor’s best route selection
For outbound traffic:
- Filter inbound routes
- Tweak attributes on inbound routes to influence best route selection
Note
In general, an AS has more control over outbound traffic
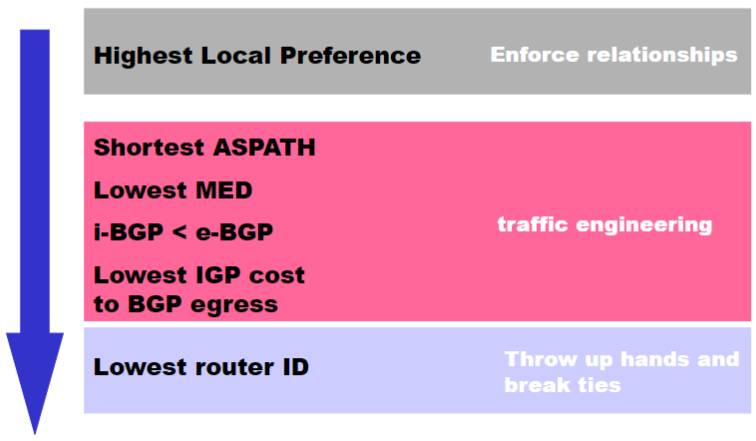
Route Selection Summary
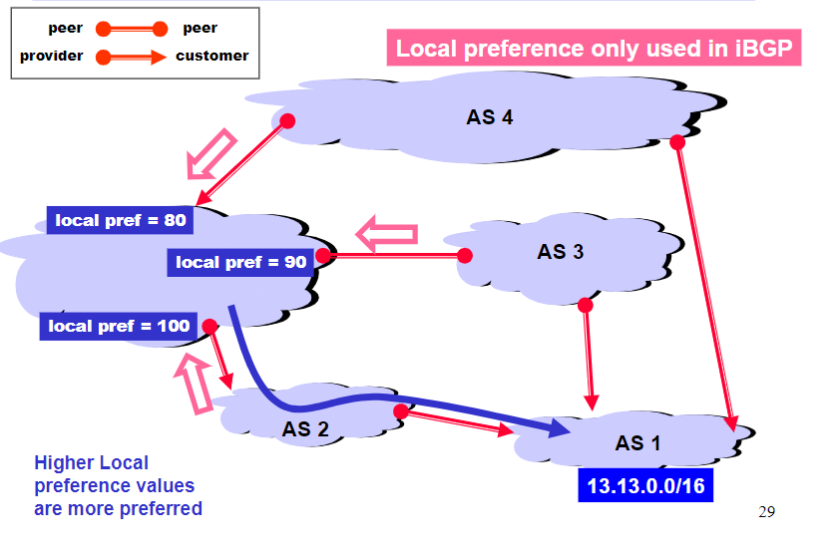
Local Preference Attribute
- Local preference attribute only used in iBGP
- Higher Local Preference values are preferred
Implementing backup links with local preference (outbound traffic)
Forces outbound traffic to take primary link, unless link is down
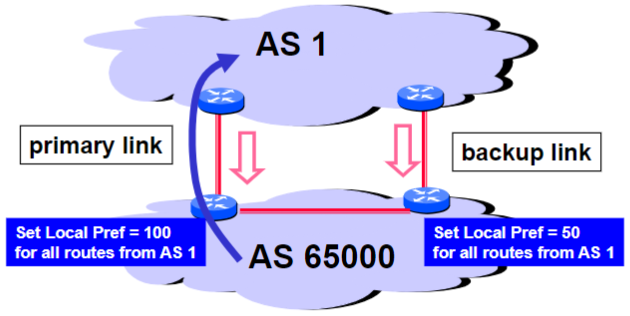
Multihomed Backups (outbound traffic):
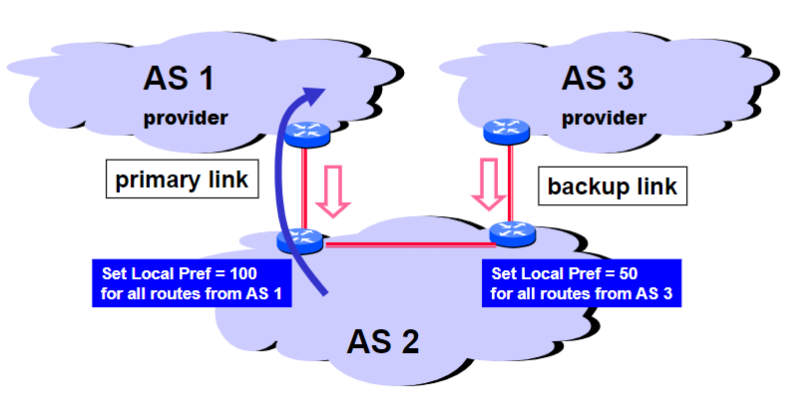
AS_PATH Attribute
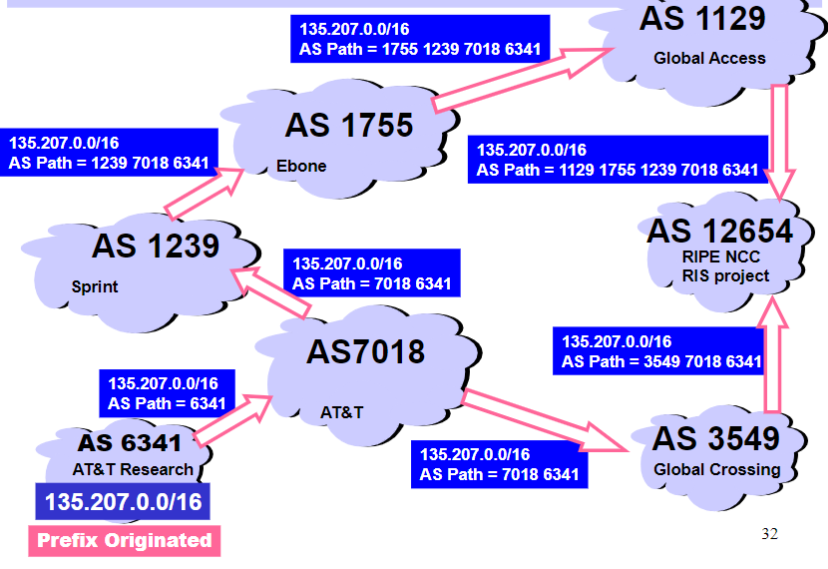
Interdomain Loop Prevention
Border gateway will never accept a route with ASPATH containing itself
- e.g. gateway at AS 877 will never accept a route with
ASPATH = 1 333 877 7018, because that would cause a cycle
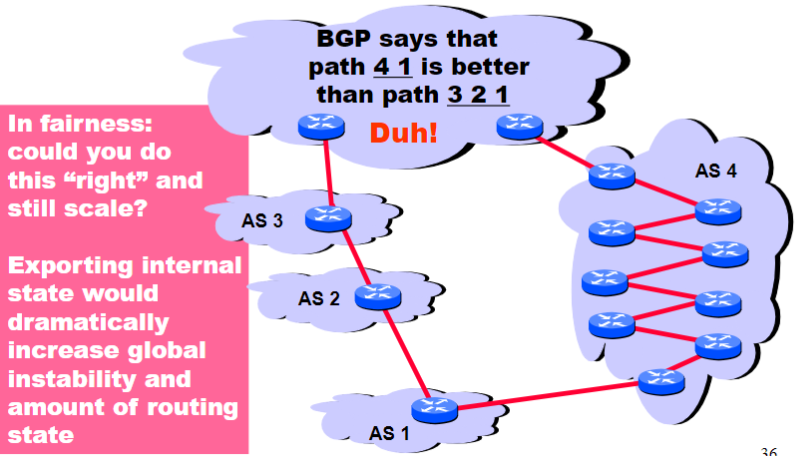
Traffic often follows AS_PATH, but not always
Traffic following AS Path:
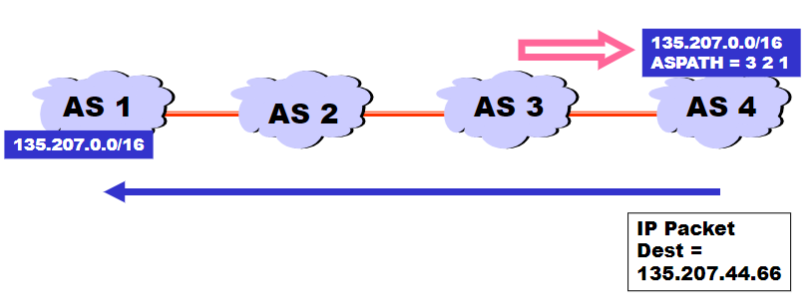
Traffic not following AS Path:
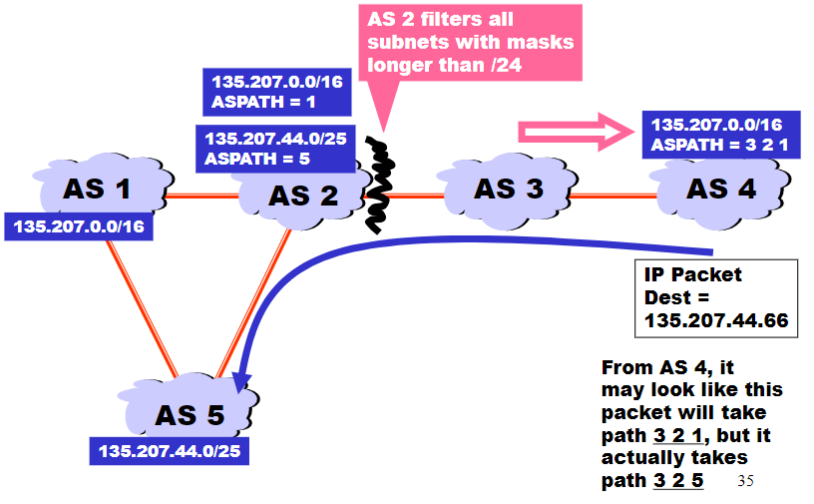
Shorter doesn’t always mean shorter
Even if the AS Path from some AS X is shorter than the AS Path from another AS Y, within the AS X, a longer path might actually be taken
- So a shorter AS Path doesn’t always mean a shorter path
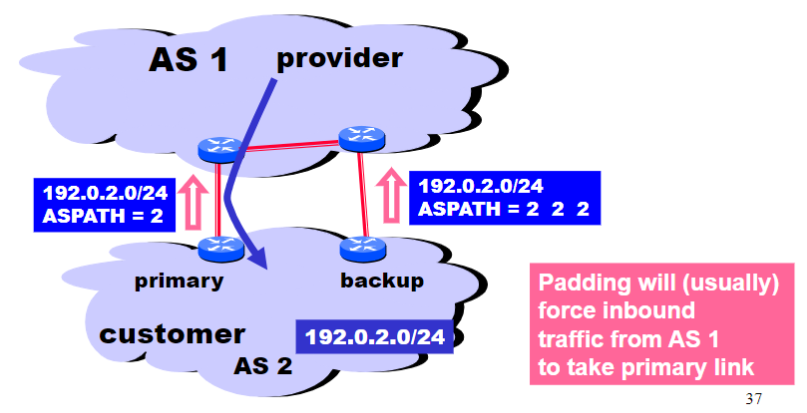
Shedding Inbound Traffic with AS_PATH Padding Hack
- Can repeat AS in
AS_PATHin backup link - Padding will usually force inbound traffic from AS 1 tot ake primary link
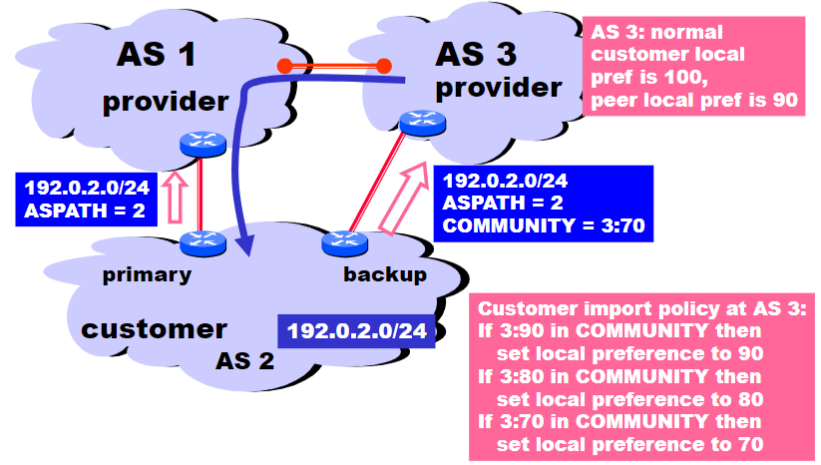
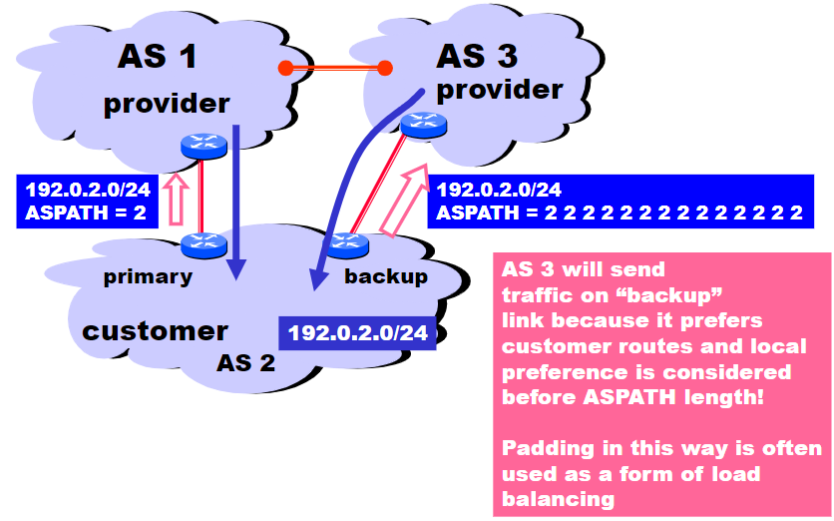
But padding may not shut off all traffic (as in the example below)
- AS 3 will send traffic on the backup link because it prefers customer routes, and local preference is prioritized over
AS_PATHlength - Padding can still be used as a form of load balancing
The COMMUNITY attribute can help in that case: