A Link Layer protocol
Modes
Two modes:
High Bit Error Rate
With wired links, most loss is due to congestion. With wireless links, there is higher loss and a time-varying bit error rate.
- Decreasing signal strength
- Disperses as it travels greater distances
- Attenuates as it passes through matter
- Interference from other sources
- Radio sources in same frequency band
- Electromagnetic noise
- Multipath propagation
- Electromagnetic waves reflect off objects
- Taking many paths of different lengths
- Causing blurring of signal at the receiver
Dealing with bit errors:
- Sender could increase transmission power
- Requires more energy (bad for battery-powered hosts)
- Creates more interference with other senders
- Stronger error detection and recovery
- More powerful error detection/correction codes
- Link-layer retransmission of corrupted frames
Broadcast Limitations
See WiFi Broadcast Limitations
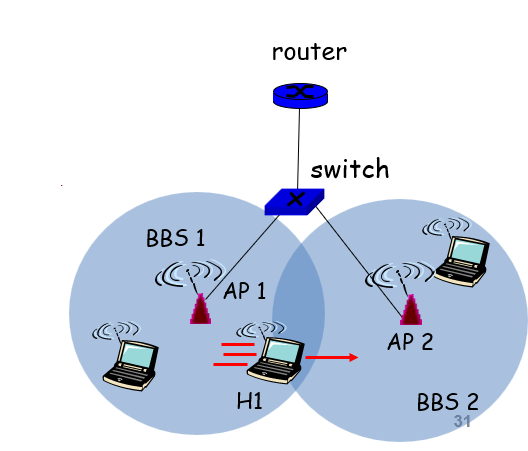
Mobility Within Same Subnet
- H1 remains in same subnet
- IP address of the host can remain same
- Ongoing data transfers can continue uninterrupted
- H1 recognizes the need to change
- H1 detects a weakening signal
- Starts scanning for a stronger one
- Changes Access Points with same SSID
- H1 disassociates from one and associates with another
- Switch learns new location
- Self-learning mechanism