To allow multiple computers to share one point
- Essentially the same as a bridge,
- but typically used to connect individual hosts rather than LANs
- Like bridges, work at Link Layer
One way of switching is Circuit switching, which was used for telephones but doesn’t work well for the Internet
Instead, Packet switching is used

Traffic Isolation
- Switch filters packets
- Frame only forwarded to the necessary segments
- Segments can support separate transmissions
Self-learning: Building the Table
Will try to learn which hosts are connected to which interfaces
When a frame arrives:
- Inspect the source MAC address
- Associate the address with the incoming interface
- Store the mapping in the switch table
- Use a timer to eventually forget the mapping
Self-learning: Handling Misses
When frame arrives with unfamiliar destination:
- Forward the frame to all the interfaces except for the ones where the frame arrived
- Hopefully, this case won’t happen often
Advantages over Repeaters
- Only forward frames as needed
- Avoid unnecessary load on segments
- Wider geographic span
- Separate segments allow longer distances
- Improves privacy
- Hosts can “snoop” traffic traversing their segment, but not the rest of the traffic
- Can join segments that use different technologies
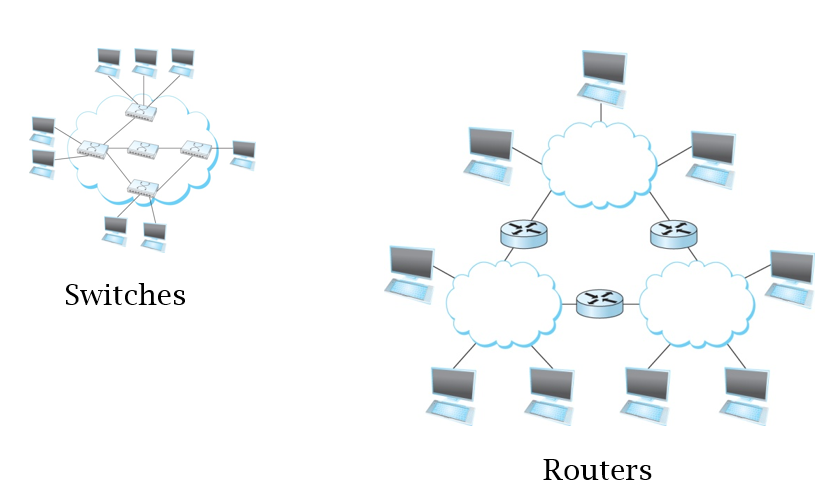
Difference between switches and routers
Switch vs Router
- Switches are link level devices used to isolate or combine physical networks
- Routers are network layer devices for IP routing and forwarding tasks
- Higher level than switches
Link to original